 Spinal bones are stacked in a column from the skull to the tailbone. They protect the spinal cord, which runs through an opening called the spinal canal. Some people are born with a small spinal canal.
Spinal bones are stacked in a column from the skull to the tailbone. They protect the spinal cord, which runs through an opening called the spinal canal. Some people are born with a small spinal canal.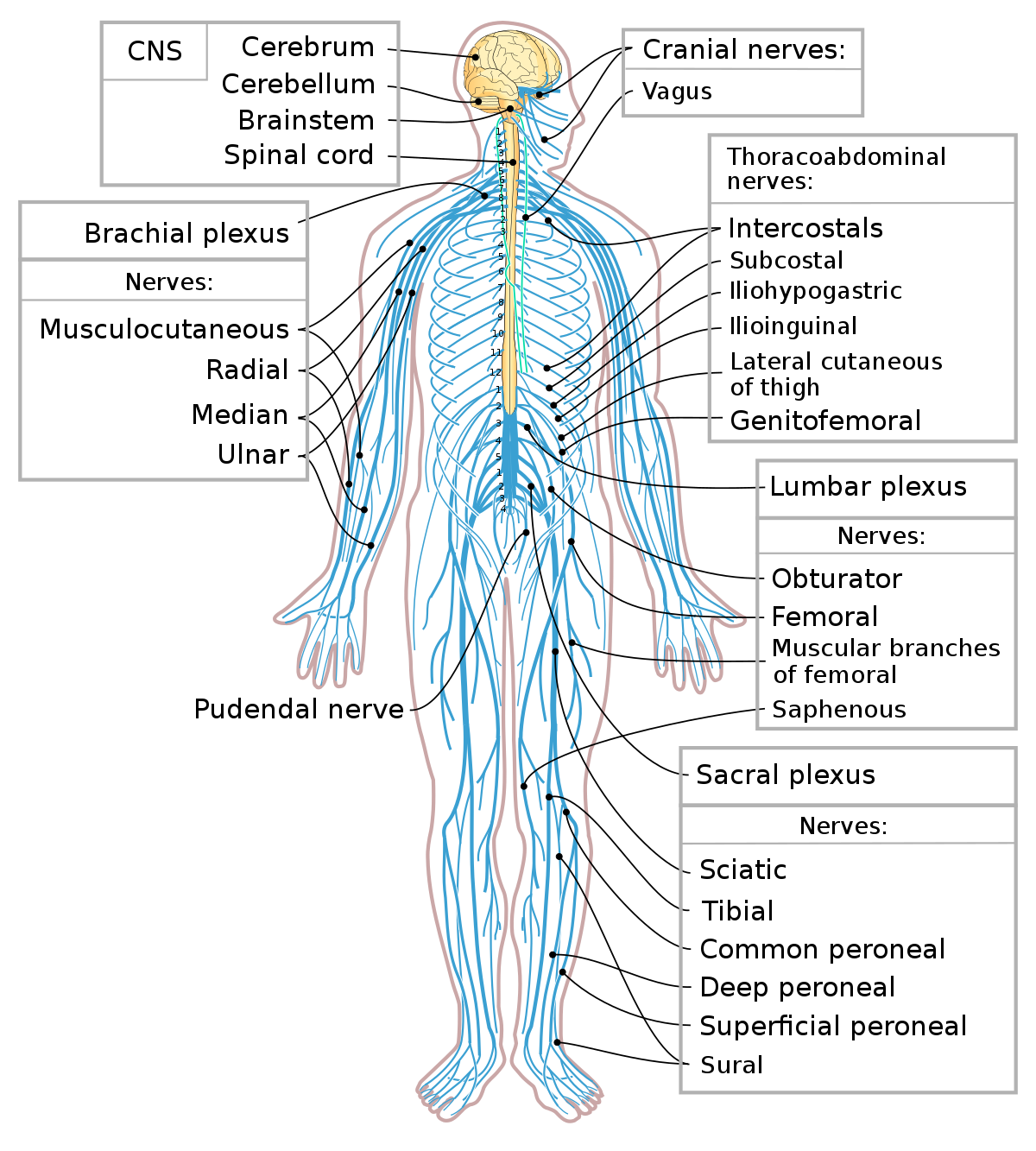 The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by the meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system.
The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by the meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system.